- -20%



It is estimated that 80% of the world's population is low in omega-3 fatty acids.
Research has shown that omega-3 fats are essential for the development, maintenance and protection of central nervous system structures from conception and undoubtedly throughout life. There is some debate about the relative importance of EPA versus DHA, but there is general scientific consensus that both EPA and DHA contribute to cognitive health and development, as well as mental well-being, learning and mood.
We know perfectly well the properties of Omega-3 acids on the cardiovascular system, or on health in general, but are we aware of how these fatty acids affect the brain, nervous system and cognitive functions?
Fats make up 60 percent of the brain and nerves that support every system in our body. So it goes without saying that the better the fat in the diet, the better our body works.
EPA and DHA are essential building blocks of healthy cell membranes. These cell membranes provide critical support for brain connectivity.
What are Omega-3s?
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential fats. Although they have many functions in our body and are important for optimal health, our body is unable to produce them, so we have to provide them with our diet or supplement them.
The three key types of omega-3 fats are:
ALA (alpha linolenic acid): present in some plant foods rich in fat, especially flax seeds, chia seeds and nuts.
EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid): found in fatty fish, seafood, fish oil and algae oil.
DHA (docosahexaenoic acid): present in oily fish, seafood, fish oils and algae oil.
Keep in mind that although ALA is an Omega-3 acid, it must be converted to longer-chain Omega-3 fatty acids such as EPA or DHA to provide all associated health benefits. Unfortunately, the human body is not very good at converting ALA. Studies show that we only convert ALA to EPA and DHA by around 5%, so supplementing them in your diet is essential. Omega-3 fatty acids are found in high concentrations in foods such as cold-water fish, flax seeds, seaweed and chia seeds. Although these foods are common, most of us don't eat enough of them.
Children who have low amounts of DHA in their diets exhibit slower brain development and reduced visual acuity.
Cultures whose diets are rich in omega 3 fatty acids (such as Eskimos who eat a lot of fish) have a lower incidence of degenerative diseases of the central nervous system such as multiple sclerosis.
Experimental animals, whose diets are low in DHA, have been found to have smaller brains and delayed central nervous system development.
Some children with poor school performance due to ADD have been shown to have insufficient amounts of essential fatty acids in their diets.
Published clinical studies suggest that the EPA has a special affinity for conditions associated with altered mood and behavior, including:
- Depression
- Bipolar affective disorder
- Schizophrenia
- HDAD
- Optimal levels of DHA phospholipids are positively correlated with the sodium-potassium pump in the mammalian brain.
Production of glutamate, dopamine, acetylcholine and serotonin has been shown to be enhanced by increased consumption of omega-3s (a change in the production or availability of neurotransmitters in the synaptic cleft likely affects nerve activity and ultimately performance. cognitive).
DHA is the most important omega-3 for brain health, accounting for 97% of the omega-3 fatty acids found in the brain.
DHA is a critical structural component of the cerebral cortex, the area of the brain responsible for memory, language, creativity, judgment, emotions and personality.
Low Omega-3 levels have been linked to anxiety, depression, and bipolar disorder. Medical students dealing with pre-exam stress showed a 20% reduction in anxiety when taking omega-3 supplements.
A review of studies in people with mood disorders showed that Omega-3 fatty acids have significant antidepressant properties. Additionally, eight weeks of EPA supplementation proved to be as
effective as Prozac in treating major depressive disorders. Conversely, when the EPA was taken alongside fluoxetine, the results were even better than taking fluoxetine or EPA alone.
Children and adolescents with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (HDAD) have lower blood levels of omega-3s, suggesting that supplementation may be helpful. A systematic review of 52 studies in children with HDAD found Omega-3 supplementation to be the most promising intervention. One study found that students taking Omega-3 performed better in reading and spelling and showed a reduction in symptoms. Another study of giving children high doses of Omega-3 fatty acids (up to 16 grams per day) found that the supplements were well tolerated and led to significant improvements in inattention, hyperactivity and behavior.
Omega-3 fats are essential for both young mothers and their babies. Postnatal depression affects 15% of all new mothers. When young mothers struggling with postpartum depression received Omega-3 supplements, they showed a reduction in symptoms of at least 50% on two standard depression scales.
Omega-3s are essential for the development of the brain and nervous system of babies and children. Getting enough omega-3s during pregnancy has numerous benefits for your baby, including reducing the risk of cerebral palsy, autism spectrum disorder, and HDAD.
Omega-3 fatty acids protect against age-related mental retardation and can aid learning and memory in adults of all ages, from the young to the 80s. Lack of omega-3 fatty acids can measurably shrink your brain and age faster. Numerous studies confirm that older adults with higher omega-3 levels, particularly DHA, have a much lower risk of developing dementia or Alzheimer's disease.
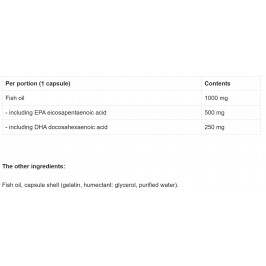
Dosage
Take 1 capusla 1 to 2 times a day with meals.